Guillem_dlc
- 188
- 17
Thread moved from the technical forums to the schoolwork forums
I have the calculation of the electric field created by a ring of radius ##R## uniformly charged with a linear density of charge ##\lambda## at any point on the axis perpendicular to its surface (##z## axis), but I have some doubts about it. I'll leave you the calculation done first:
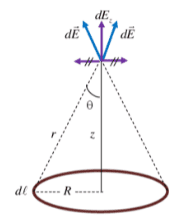
In ##x## axis the field is ##0##. We calculate the electric field:
$$dE=k\dfrac{dq}{r^2}\rightarrow dq=\lambda dl$$
$$E=k\int_0^L \dfrac{\lambda dl}{r^2}=\dfrac{k\lambda}{r^2}\int_0^L dl=\dfrac{k\lambda}{r^2}2\pi R$$
because we have a ring: ##2\pi R##
$$E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi \varepsilon_0}\dfrac{2\pi R}{r^2}=\dfrac{\lambda}{2\varepsilon_0}{R}{r^2}=\dfrac{\lambda R}{2\varepsilon_0 r^2}$$
$$E_z=E\cdot \cos \alpha =E\cdot \dfrac{z}{r}=\dfrac{\lambda}{2\varepsilon_0}\dfrac{zR}{r^3}=\dfrac{\lambda zR}{2\varepsilon_0 (z^2+R^2)^{3/2}}$$
because $r=\sqrt{z^2+R^2}$.
Question: I have problems with these exercises with integrals. For example, I understand this, but the drawing of the principle I don't see because it takes two instead of one and in the integral I don't understand because in some exercises there are things that are constant and things that are not.
In ##x## axis the field is ##0##. We calculate the electric field:
$$dE=k\dfrac{dq}{r^2}\rightarrow dq=\lambda dl$$
$$E=k\int_0^L \dfrac{\lambda dl}{r^2}=\dfrac{k\lambda}{r^2}\int_0^L dl=\dfrac{k\lambda}{r^2}2\pi R$$
because we have a ring: ##2\pi R##
$$E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi \varepsilon_0}\dfrac{2\pi R}{r^2}=\dfrac{\lambda}{2\varepsilon_0}{R}{r^2}=\dfrac{\lambda R}{2\varepsilon_0 r^2}$$
$$E_z=E\cdot \cos \alpha =E\cdot \dfrac{z}{r}=\dfrac{\lambda}{2\varepsilon_0}\dfrac{zR}{r^3}=\dfrac{\lambda zR}{2\varepsilon_0 (z^2+R^2)^{3/2}}$$
because $r=\sqrt{z^2+R^2}$.
Question: I have problems with these exercises with integrals. For example, I understand this, but the drawing of the principle I don't see because it takes two instead of one and in the integral I don't understand because in some exercises there are things that are constant and things that are not.