Fatima Hasan
- 315
- 14
- Homework Statement
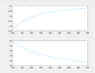
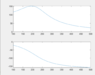
- Consider the simple ac circuit of figure 1(b). The frequency of the AC source varies between 100 Hz to 500 Hz. Draw the magnitude and phase angle of the voltage across the capacitor. Try to increase the frequency by step of 5 Hz.
The circuit is attached below.
- Relevant Equations
- -
My solution is attached below.
I am not sure if my answer is correct or not , I want to confirm it.
I am not sure if my answer is correct or not , I want to confirm it.