- #1
denny2
- 1
- 0
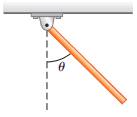
One end of a thin, uniform rod is connected to a frictionless hinge as shown in Figure 1. The rod has a length of 0.8 mand a mass of 2 kg. It is held up in the horizontal position (θ=90∘) and then released.
1)Calculate the angular velocity of the rod at θ=90∘.
2)Calculate the angular acceleration of the rod at θ=90∘.
3)Calculate the angular velocity of the rod at θ=60∘
4)Calculate the angular acceleration of the rod at θ=60∘
5)Calculate the angular velocity of the rod at θ=0∘.
6)Calculate the angular acceleration of the rod at θ=0∘.
mgh=1/2 Iw^2
a = ((mgcos)1/2)/I
I got these answers and only 1 and 6 were correct
1)0 rad/s
2)74 rad/s^2
3)8.6 rad/s
4)64 rad/s^2
5)12 rad/s
6)0 rad/s^2
Any help is appreciated thank you :)
1)Calculate the angular velocity of the rod at θ=90∘.
2)Calculate the angular acceleration of the rod at θ=90∘.
3)Calculate the angular velocity of the rod at θ=60∘
4)Calculate the angular acceleration of the rod at θ=60∘
5)Calculate the angular velocity of the rod at θ=0∘.
6)Calculate the angular acceleration of the rod at θ=0∘.
Homework Equations
mgh=1/2 Iw^2
a = ((mgcos)1/2)/I
The Attempt at a Solution
I got these answers and only 1 and 6 were correct
1)0 rad/s
2)74 rad/s^2
3)8.6 rad/s
4)64 rad/s^2
5)12 rad/s
6)0 rad/s^2
Any help is appreciated thank you :)