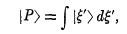Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the representation of a general ket in quantum mechanics using a basis of eigenkets associated with a continuous range of eigenvalues. Participants explore the mathematical formulation and implications of using integrals in this context, particularly in relation to discrete versus continuous eigenvalue spectra.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant questions the role of the integral in representing a general ket using eigenkets from a continuous range of eigenvalues, comparing it to a sum in the discrete case and expressing confusion about the meaning of the infinitesimal change near the eigenvalue.
- Another participant references a related thread on Rigged Hilbert Spaces, suggesting it may provide additional insights into the relationship between continuous and discrete bases.
- A participant proposes that the continuous basis can be seen as a limiting case of the discrete basis, noting that normalization conventions change when transitioning between the two.
- Concerns are raised about the conditions necessary for the continuum limit to be valid, including assumptions about the ordering and completeness of eigenvalues and eigenstates.
- There is a discussion on the normalization of kets in the continuous case, with a participant suggesting that if the coefficients change slowly, a new ket can be defined with a different normalization that leads to an integral representation.
- One participant explains that the differential dλ is introduced to ensure the product between each eigenket and dλ remains finite, given the infinite length of the eigenkets in the limit of Δλ approaching zero.
- Another participant expresses skepticism about the use of infinitesimals in this context, suggesting that a proper understanding requires studying distribution theory.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying levels of understanding and agreement regarding the mathematical treatment of eigenkets and the implications of using integrals versus sums. There is no consensus on the interpretation of infinitesimals or the normalization of kets in the continuous case.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight limitations in their understanding of the transition from discrete to continuous eigenvalues, including assumptions about the behavior of eigenstates and the implications of normalization conventions.