SUMMARY
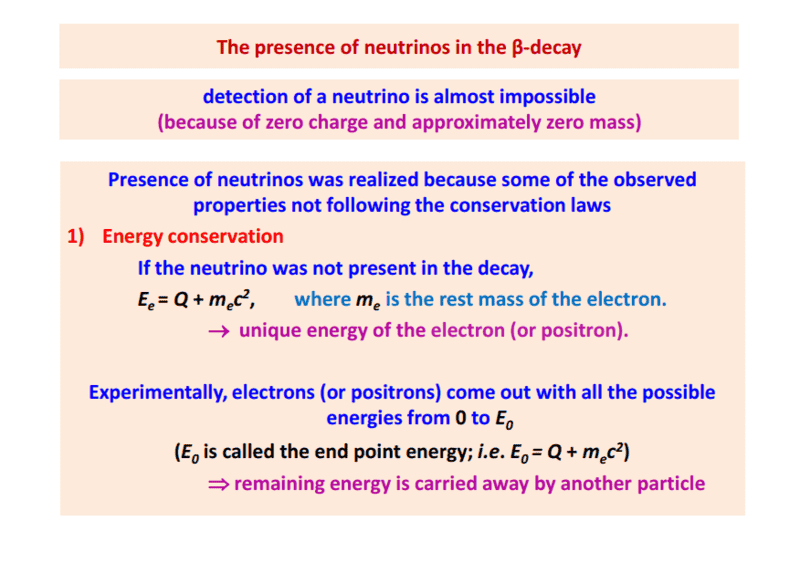
The discussion centers on the concept of endpoint energy in beta decay, specifically the relationship between the Q value and the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electron. The Q value is defined as the difference between the total initial mass-energy and the total final mass-energy of the decay products. The endpoint energy, denoted as E0, is clarified to be E0 = Q + mec2, where me is the rest mass of the electron. This indicates that endpoint energy encompasses both the maximum kinetic energy and the rest mass energy of the electron, rather than being solely the maximum kinetic energy observed.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of beta decay and its mechanisms.
- Familiarity with the concepts of mass-energy equivalence and Q value.
- Basic knowledge of particle kinematics and energy conservation principles.
- Ability to interpret relativistic energy equations.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Q value in beta decay processes.
- Learn about the implications of mass-energy equivalence in particle physics.
- Explore the concept of endpoint energy in greater detail through resources like Nucleonica.
- Investigate the role of neutrinos in beta decay and their impact on energy calculations.
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, students of nuclear physics, and anyone interested in understanding the intricacies of beta decay and energy calculations in particle interactions.