SUMMARY
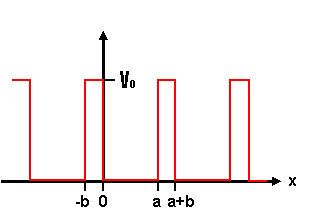
The discussion focuses on the Kronig-Penney Model, specifically addressing the solutions to the time-independent Schrödinger equation within and outside a periodic potential. In the region of -b < x < 0, the potential V(x) = V0 leads to real exponential solutions, indicating wavefunction decay, while in the region of 0 < x < a, the potential V = 0 results in complex exponentials representing traveling waves. The boundary conditions applied yield a determinant condition for allowed energy values, which is crucial for understanding band structure diagrams as outlined in Kittel's 8th Edition.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the time-independent Schrödinger equation
- Familiarity with the Kronig-Penney Model
- Knowledge of boundary conditions in quantum mechanics
- Concepts of allowed and forbidden energy values in band theory
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Kronig-Penney Model solutions
- Learn about Bloch's Theorem and its implications for wavefunctions
- Explore the concept of band structure diagrams in solid-state physics
- Investigate the mathematical techniques for solving second-order ordinary differential equations
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in physics, particularly those specializing in quantum mechanics and solid-state physics, will benefit from this discussion, especially those interested in understanding energy bands and wavefunction behavior in periodic potentials.