naman chauhan
- 14
- 0
Hi everyone,

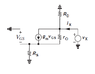
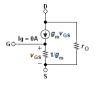
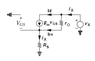
I have attached an image of fet amplifier in common source configuration. I want to have the ac analysis of this circuit. I am able to figure out the input impedance and the voltage gain. But I can't formulate for output impedance.
According to me, while calculating output impedance input should be zero. As soon as vs becomes zero the value of current (gm Vgs) will be zero. So the current source will behave as an open circuit. And we get (Rd||rd). But according to book it's wrong.
Can anybody help!
Thanks in advance.
I have attached an image of fet amplifier in common source configuration. I want to have the ac analysis of this circuit. I am able to figure out the input impedance and the voltage gain. But I can't formulate for output impedance.
According to me, while calculating output impedance input should be zero. As soon as vs becomes zero the value of current (gm Vgs) will be zero. So the current source will behave as an open circuit. And we get (Rd||rd). But according to book it's wrong.
Can anybody help!
Thanks in advance.