Discussion Overview
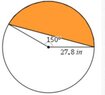
The discussion revolves around finding the area of a shaded region formed by two shapes: a circular sector and an isosceles triangle. Participants explore the mathematical approach to calculate the shaded area, including the necessary formulas and values.
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses confusion about a problem involving two shapes and seeks assistance.
- Another participant proposes a method to find the shaded area by subtracting the area of the isosceles triangle from the area of the circular sector, providing the relevant formulas.
- A participant requests clarification on the angle represented by "θ," which is explained as a Greek letter commonly used for angles.
- One participant shares their calculated values for the areas of the triangle and the sector, along with the resulting shaded area.
- Another participant reformulates the area calculation using the provided values for radius and angle, confirming their result with a numerical approximation.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
There is no explicit consensus on the correctness of the calculations or methods, as participants are sharing different approaches and results without resolving potential discrepancies.
Contextual Notes
Participants reference specific values for radius and angle, but the discussion does not clarify the assumptions or conditions under which these values are applied. There may be unresolved mathematical steps in the calculations presented.