SUMMARY
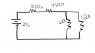
The discussion focuses on calculating the current and voltage across resistors in a circuit with a total voltage of 24V and resistances of R1=270 ohms, R2=330 ohms, and two resistors of R3=1.2k ohms and R4=1.2k ohms. The calculated currents are IR1=20mA, IR2=20mA, IR3=10mA, and IR4=10mA. The participants clarify that R1 and R2 are in series with the combined resistance of R3 and R4, which are in parallel, leading to an effective resistance of 600 ohms.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ohm's Law
- Knowledge of series and parallel resistor combinations
- Familiarity with calculating equivalent resistance
- Basic circuit analysis techniques
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of series and parallel circuits
- Learn how to calculate equivalent resistance in complex circuits
- Explore Ohm's Law applications in circuit analysis
- Investigate voltage division and current division rules
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electrical engineering, hobbyists working on circuit design, and anyone looking to improve their understanding of resistor networks and circuit analysis.