SUMMARY
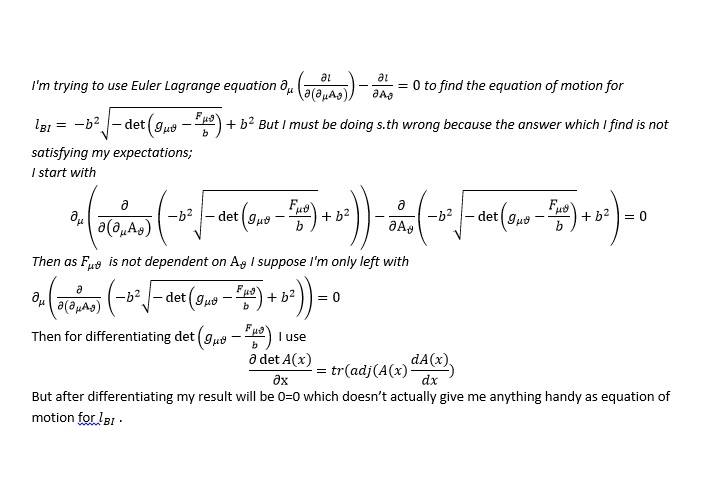
The discussion focuses on deriving the equation of motion for the Born-Infeld Lagrangian, specifically for a scalar field $\phi$. The Lagrangian is defined as $$L=\sqrt{1+\partial_\mu\phi\partial^\mu\phi}-V(\phi)$$, where $V(\phi)$ represents the scalar field's potential. The equation of motion is derived using the Euler-Lagrange equation, resulting in $$\partial_\mu\left(\frac{\partial_\mu\phi}{\sqrt{1+\partial_\nu \phi \partial^\nu \phi}}\right) - \frac{dV}{d\phi}=0$$.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the Born-Infeld Lagrangian
- Familiarity with the Euler-Lagrange equation
- Knowledge of scalar field theory
- Basic calculus and differential equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Euler-Lagrange equation in detail
- Explore the implications of the Born-Infeld Lagrangian in field theory
- Investigate potential functions $V(\phi)$ and their effects on motion
- Learn about variations in Lagrangian mechanics
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, particularly those specializing in field theory, graduate students studying advanced mechanics, and researchers exploring non-linear field theories will benefit from this discussion.