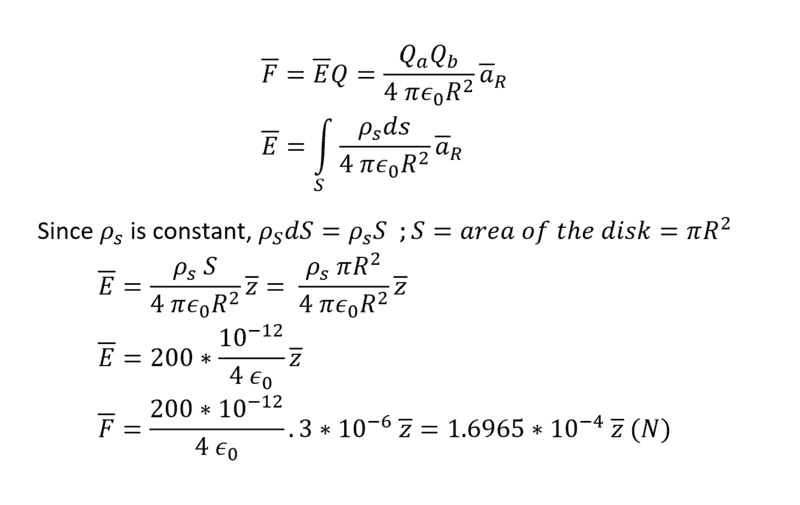Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the force acting on a point charge with a disk surrounding it. Participants explore the relevant equations and clarify the parameters involved, including the geometry of the disk and the calculations leading to the force result.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant presents a force calculation resulting in F = -99.4 az μN and requests assistance in identifying any mistakes.
- Another participant seeks clarification on the meaning of R in the equation for electric field E.
- A subsequent reply confirms that R refers to the radius.
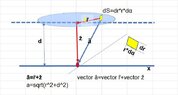
- Concerns are raised about the clarity of the disk's position, questioning whether the center is on the z-axis or displaced, and the exact dimensions of the disk.
- A participant outlines a detailed calculation process for the electric field E, including integrals and assumptions about symmetry, leading to a derived force value of approximately 99.4 μN.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express uncertainty regarding the disk's position and dimensions, and there is no consensus on the correctness of the initial force calculation or the clarity of the problem setup.
Contextual Notes
The discussion highlights potential ambiguities in the problem statement, including the definitions of parameters and the assumptions made in the calculations. The mathematical steps and their dependencies are not fully resolved.