- #1
t0mm02
- 49
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Estimate what the Reynolds number is of the fluid flowing around the table
- Relevant Equations
- Reynolds number
I have to estimate the Reynolds number of the fluid flowing around a blade but I only have one detail: the length of the blade is 0.66m.
I have no idea how to do it and I got to submit the assignment in a week, I am desperate for help here.
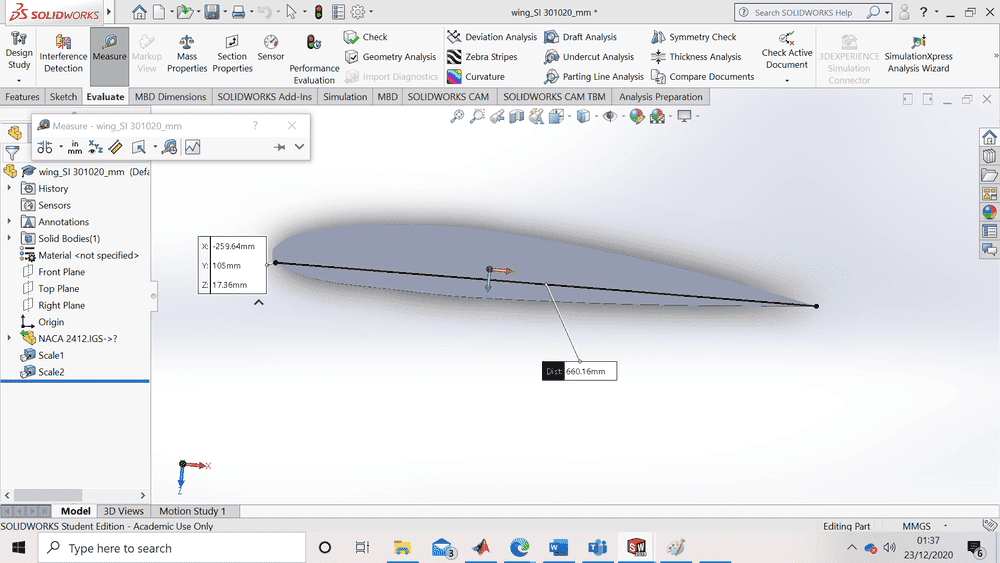
I have no idea how to do it and I got to submit the assignment in a week, I am desperate for help here.