Tesla In Person
- 34
- 13
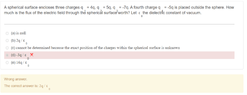
- Homework Statement
- What is the flux of electric field through sphere with charges inside and outside of the sphere?
- Relevant Equations
- Electric field flux = Q/ e0
My attempt: We have 3 charges inside 2 +ve and 1 -ve so i just added them up. 4 + 5 +(-7) = 2q
Then there is a -5q charge outside the sphere. I did 2q + (-5q)= -3q . The electric field flux formula is Flux= q/ E0 . So i got -3q/E0 which is obviously wrong : ) . After quick googling , I discovered that the electric flux through a sphere is only dependent on charges enclosed by the sphere , charges outside don't affect electric flux through sphere. Is it correct and why it is the case? I am not familiar with Gauss' law so how do i get started. Thank you
Then there is a -5q charge outside the sphere. I did 2q + (-5q)= -3q . The electric field flux formula is Flux= q/ E0 . So i got -3q/E0 which is obviously wrong : ) . After quick googling , I discovered that the electric flux through a sphere is only dependent on charges enclosed by the sphere , charges outside don't affect electric flux through sphere. Is it correct and why it is the case? I am not familiar with Gauss' law so how do i get started. Thank you