so_gr_lo
- 69
- 10
- Homework Statement
- End B of uniform rod of length 1.5 weight 30N rests against smooth surface inclined at 70°. Other end, A, of rod rests on rough ground at 50°. Find the magnitude of the force acting at B.
- Relevant Equations
- moment = F x d
Question diagram, attempt at solution below
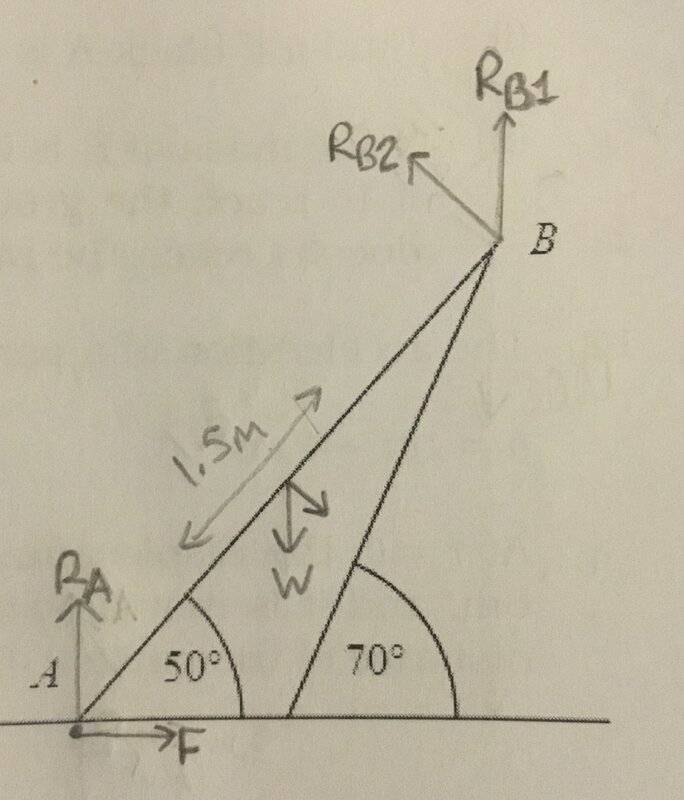

I need to cancel some of the terms in the moment equation but a not sure which ones to start with. I don’t know μ so can not calculate FA, so should probably substitute FA = RB2.
I need to cancel some of the terms in the moment equation but a not sure which ones to start with. I don’t know μ so can not calculate FA, so should probably substitute FA = RB2.