Homework Help Overview
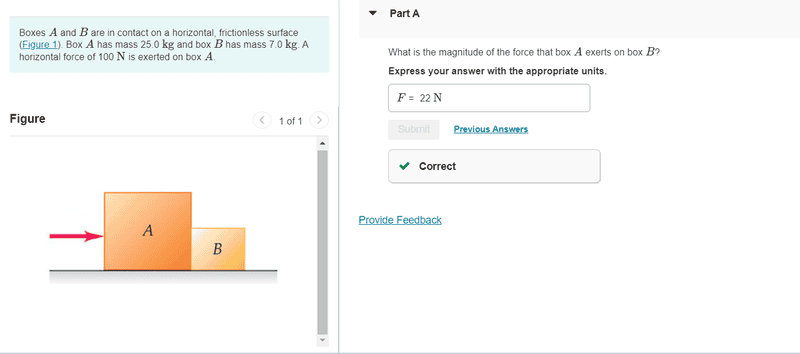
The discussion revolves around the forces exerted between two blocks on a frictionless surface, specifically focusing on the force that Block A exerts on Block B. The subject area includes concepts from dynamics and Newton's laws of motion.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
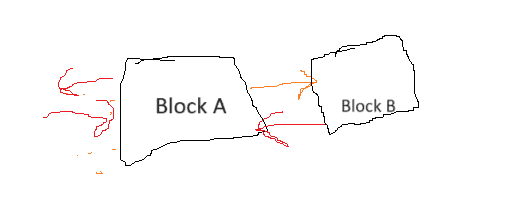
- Participants explore the reasoning behind using the mass of Block B to determine the force exerted by Block A, questioning the role of Block B's inertia and mass in this context. There are suggestions to draw free body diagrams to clarify the forces acting on each block.
Discussion Status
The discussion is active with participants raising questions about the assumptions involved in the problem, particularly regarding the relationship between the masses of the blocks and the forces acting on them. Some guidance on using free body diagrams has been mentioned, indicating a productive direction in the conversation.
Contextual Notes
There is an implicit assumption about the frictionless nature of the surface and the interaction between the two blocks, which may influence the analysis of forces. The varying mass of Block B is also a point of consideration in understanding the dynamics at play.