- 24,488
- 15,057
Has anybody a translation for the various cones describing the motion of the free symmetric top?
The German expressions are "Nutationskegel" (space-fixed cone via the precession of the body-fixed symmetry axis ##\vec{e}_3'##) , and "Rastpolkegel" (space-fixed cone via the precession of the angular velocity ##\vec{\omega}## around the constant angular momentum), and "Gangpolkegel" (body-fixed cone via the precession of ##\vec{\omega}## around ##\vec{e}_3'##) as nicely depicted in the German Wikipedia:
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler-Kreisel#Beschreibung_der_Bewegung
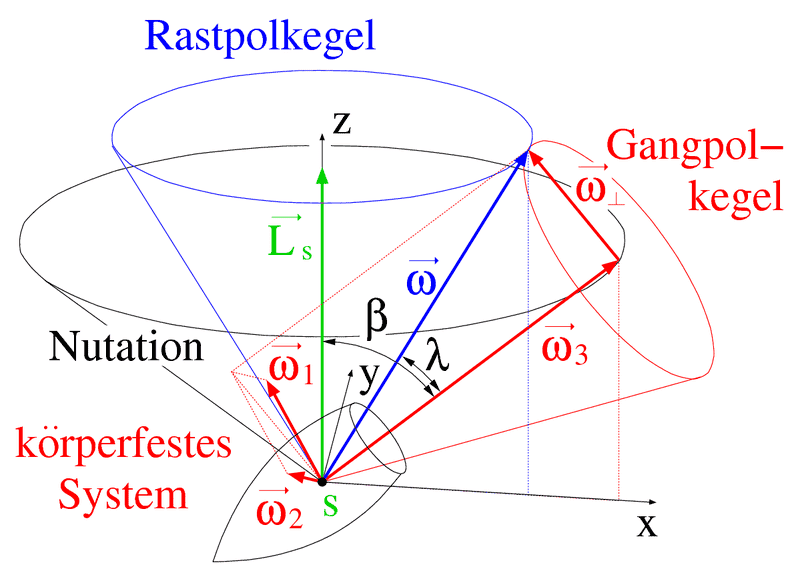
Surprisingly, I couldn't find a similar figure nor the names of these cones in the English-speaking literature.
The German expressions are "Nutationskegel" (space-fixed cone via the precession of the body-fixed symmetry axis ##\vec{e}_3'##) , and "Rastpolkegel" (space-fixed cone via the precession of the angular velocity ##\vec{\omega}## around the constant angular momentum), and "Gangpolkegel" (body-fixed cone via the precession of ##\vec{\omega}## around ##\vec{e}_3'##) as nicely depicted in the German Wikipedia:
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler-Kreisel#Beschreibung_der_Bewegung
Surprisingly, I couldn't find a similar figure nor the names of these cones in the English-speaking literature.