Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the interaction of circles and parallel lines in geometry, specifically addressing a problem related to areas of shaded and unshaded regions. The scope includes conceptual understanding and problem-solving techniques.
Discussion Character
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses confusion about how to approach the geometry problem presented.
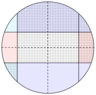
- Another participant shares a visual aid, suggesting it may clarify the situation.
- A participant questions whether solving the problem involves using fractions, indicating uncertainty about the method.
- Another participant calculates an area as 32 square units but notes difficulty in understanding the full context of shaded versus unshaded areas.
- One participant suggests that "cancelling" the dotted areas with the corresponding shaded areas results in a simpler rectangle, which they claim represents the difference in areas.
- A later reply expresses relief and gratitude for the assistance received, indicating a positive experience with the forum.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
The discussion reflects multiple viewpoints and uncertainties regarding the problem-solving approach, with no clear consensus reached among participants.
Contextual Notes
Participants express varying levels of understanding and confidence in their approaches, with some calculations and methods remaining unverified or unresolved.
Who May Find This Useful
Individuals interested in geometry, particularly those seeking help with area calculations and the interaction of geometric shapes.