- #1
Turion
- 145
- 2
How do the effects of semiconductor semiconductor doping affect the Hall effect?
For instance, consider number 4 and 5 in the following sample:
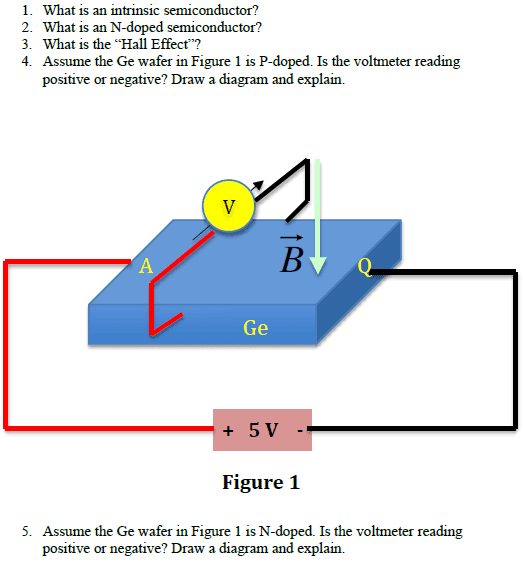
Using the right hand rule, B points downwards, conventional current points to the right (because of the 5V battery), and therefore, the force on electrons points into the page. Electrons are going into the page from the red wire to the black wire and conventional current is going from the black wire to the red wire. But when conventional current goes from ground (black wire) to the higher voltage (red wire), then the voltage must be negative. Therefore, the voltmeter would read a negative reading.
However, I am unsure what kind of effects doping the semiconductor would have on the voltmeter.
For instance, consider number 4 and 5 in the following sample:
Using the right hand rule, B points downwards, conventional current points to the right (because of the 5V battery), and therefore, the force on electrons points into the page. Electrons are going into the page from the red wire to the black wire and conventional current is going from the black wire to the red wire. But when conventional current goes from ground (black wire) to the higher voltage (red wire), then the voltage must be negative. Therefore, the voltmeter would read a negative reading.
However, I am unsure what kind of effects doping the semiconductor would have on the voltmeter.