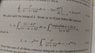You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
I How does ε disappear from the equation?
- I
- Thread starter Tomtam
- Start date
AI Thread Summary
The discussion centers on the disappearance of ε from equation (5.197) when taking the limit as ε approaches zero. Participants emphasize the need for clarity and context in the question, noting that the absence of a limit in the original post may explain the confusion. The importance of proper formatting, such as using LaTeX instead of unclear images, is highlighted to facilitate better responses. Additionally, the conversation touches on the etiquette of posting questions, advising against using bold or capital letters, which can be perceived as shouting. Overall, providing more details and context is crucial for receiving effective assistance.
Mathematics news on Phys.org
jedishrfu
Mentor
- 15,470
- 10,180
Welcome to PF!
There's not enough context to answer your question.
What does epsilon represent? is it part of a limit where epsilon goes to zero?
I didn't see any limit mentioned in the photo but that might explain why the epsilon term is removed.
There's not enough context to answer your question.
What does epsilon represent? is it part of a limit where epsilon goes to zero?
I didn't see any limit mentioned in the photo but that might explain why the epsilon term is removed.
- 20,677
- 27,972
Let me first clarify something: Am I right, that you expect more effort made in an answer than you spent to prepare your question? And as if this wasn't enough, you yell at those who are willing to deal with your question?Tomtam said:how does ε disappear from the equation (5.197) ,if we take limit ε to zero?
jedishrfu
Mentor
- 15,470
- 10,180
So ##i \epsilon## is the imaginary component of the complex number ##(x +i \epsilon)## ?
Tomtam
yesjedishrfu said:So ##i \epsilon## is the imaginary component of the complex number ##(x +i \epsilon)## ?
jedishrfu
Mentor
- 15,470
- 10,180
Okay, I think @fresh_42 is better equipped to answer this.
One thing I'd like to point out here is that its bad form to write your question in bold lettering (or capitalized lettering) as it is seen as yelling by readers of your post.
Second thing is that you need to provide the context right up front as we don't know where you are coming from and then have to ask delaying a good response to your question.
Third things is you need to write your post in Latex instead of posting poor quality phone photos where its somewhat hard to read. Also it would be helpful if you used the homework template and tell us what level of math you are studying and what book you are using.
One thing I'd like to point out here is that its bad form to write your question in bold lettering (or capitalized lettering) as it is seen as yelling by readers of your post.
Second thing is that you need to provide the context right up front as we don't know where you are coming from and then have to ask delaying a good response to your question.
Third things is you need to write your post in Latex instead of posting poor quality phone photos where its somewhat hard to read. Also it would be helpful if you used the homework template and tell us what level of math you are studying and what book you are using.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 741
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 10
- Views
- 3K
Hot Threads
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 105
- General Math
-
B What could prove this wrong? I'm having a dispute with friends
- Started by ducknumerouno
- Replies: 94
- General Math
-
B About a definition: What is the number of terms of a polynomial P(x)?
- Started by littlemathquark
- Replies: 48
- General Math
-
B How Many Straight Lines to Connect an N by M Array of Points in a Closed Loop?
- Started by bob012345
- Replies: 25
- General Math
-
B Geometry Puzzle with 20 points in a cross pattern
- Started by bob012345
- Replies: 31
- General Math
Recent Insights
-
Insights Why Entangled Photon-Polarization Qubits Violate Bell’s Inequality
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 26
- Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 11
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 1
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 105
- General Math