Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the torque required for a steel ball to move upwards at a uniform speed within a spiral tube. Participants explore various parameters and conditions affecting the torque calculation, including the geometry of the spiral tube and the forces acting on the ball.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant proposes a formula for torque when the steel ball is absent, suggesting torque depends on the masses and friction involved.
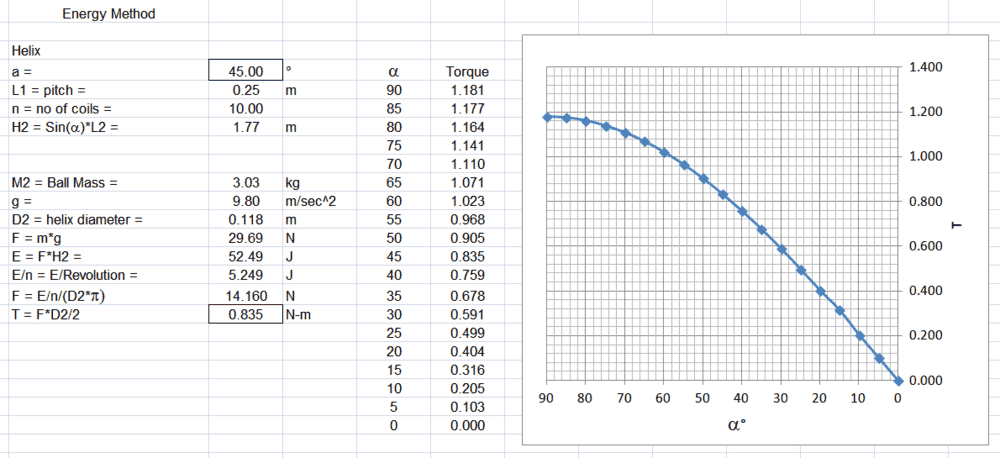
- Another participant suggests using conservation of energy to find the torque induced by the steel ball.
- Concerns are raised about the support structure of the shaft, questioning whether there is a bearing at the top end.
- Some participants argue that the steel ball may not exert a force to rotate the spiral tube if it remains at the lowest point of the spiral.
- A participant clarifies that the torque calculation involves breaking down the forces acting on the ball into components parallel and perpendicular to the shaft centerline.
- There is a discussion about the angle of the helix and its relation to the torque calculation, with some participants suggesting different interpretations of the parameters involved.
- One participant notes that the inertia of certain components only affects the torque during startup, not during continuous operation.
- Another participant expresses confusion about specific terms in the torque calculation and suggests alternative ways to express the angle of the helix.
- Participants discuss the energy required to lift the ball and relate it to power and torque, but some express difficulty in determining the power needed for the system.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
There is no consensus on the exact method for calculating the torque, with multiple competing views and interpretations of the parameters involved. Participants express differing opinions on the role of the steel ball and the effects of the spiral tube's geometry.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight the complexity of the system, including the dependence on various parameters such as the angle of the helix, the presence of friction, and the specific geometry of the spiral tube. Some assumptions about the system's behavior remain unresolved.
Who May Find This Useful
Individuals interested in mechanical engineering, physics of motion, or those working on similar machinery involving torque calculations may find this discussion relevant.