Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around implementing precise timing delays in PWM code for controlling a DC motor using the PIC16F84A microcontroller. Participants explore how to achieve specific delays of 25 microseconds, 50 microseconds, and 75 microseconds within a 100 microsecond cycle, focusing on coding strategies and timing mechanisms.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
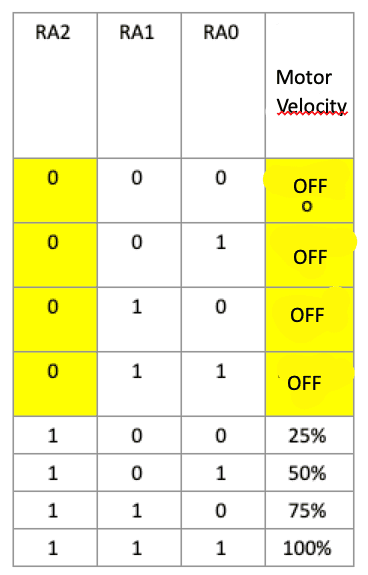
- One participant suggests using a state machine approach with conditional delays based on the state read from PortA, proposing specific delay times for each state.
- Another participant emphasizes writing straight code with unconditional equal delays, indicating that the total delay in the loop should equal 100 microseconds.
- There is a suggestion that an in-line delay may be more efficient than using a timer for the 25 microsecond delay, with a proposed code snippet for achieving this.
- A participant discusses the conversion of a 3-bit state representation into a 4-column format to simplify the PWM generation process, suggesting specific bit manipulations for output to the motor.
- Some participants express uncertainty about the efficiency of achieving the required delays and the best approach to implement the PWM logic.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants have not reached a consensus on the best method to implement the delays and PWM control. Multiple competing views and approaches remain, with some participants advocating for different coding strategies and delay mechanisms.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved aspects regarding the efficiency of the proposed delay methods and the implications of using different coding strategies on the overall performance of the PWM control. Specific assumptions about the timing and state representation are also present but not fully explored.