SUMMARY
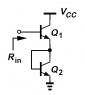
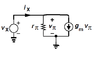
The input impedance of a BJT amplifier circuit was analyzed, specifically focusing on the input resistance calculation. The derived formula for input resistance (Rin) is Rin = 1/gm, where gm represents the transconductance of the transistor. The discussion clarified that the input resistance is influenced by the diode-connected transistor Q2, which affects the total resistance due to its collector and base current interactions. The equivalent circuit approach was utilized to derive the relationship between input voltage and current, leading to the final expression for Rin.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of BJT transistor operation and characteristics
- Familiarity with small-signal models, specifically rbe and gm
- Knowledge of equivalent circuit analysis techniques
- Basic principles of input impedance in amplifier circuits
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of transconductance (gm) in BJT amplifiers
- Learn about small-signal analysis in transistor circuits
- Explore the impact of feedback on input impedance in amplifiers
- Investigate the role of β (beta) in BJT performance and input resistance
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone involved in the analysis and design of BJT amplifier circuits will benefit from this discussion.