Clandry
- 74
- 0
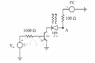
I just wanted to see if I am understanding this circuit correctly.
Let's say the input voltage (V_in) is 0.
This means:
1) no current through the 1000 ohm resistor
2) no 0.7V drop from the base to emitter
3) transistor is pretty much off
4) The circuit is open, thus no current goes through the 100 ohm resistor either
5) voltage at A must be 5V
Let's say the input voltage (V_in) is 0.
This means:
1) no current through the 1000 ohm resistor
2) no 0.7V drop from the base to emitter
3) transistor is pretty much off
4) The circuit is open, thus no current goes through the 100 ohm resistor either
5) voltage at A must be 5V