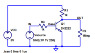
- #1
Mohamed Abdul
Homework Statement
1. In Figure A-1 of Experiment 18, assume that Vdc = 8Volts, R1 = 1kOhms, R3 = 7kOhms and there is no R2 resistor. Determine the current in R1 when the transistor is fully on and carrying current. Express your answer in mA.
2. In the circuit of Figure A-1, Experiment 18, assume that Vdc = 19Volts, R1 = 4kOhms, R2 = 26kOhms and R3 = 5kOhms. When the transistor is off, determine the output voltage (also the collector voltage) in Volts.
The figure in question is here:
Homework Equations
When the transistor of a circuit is off, current is 0 amps.
When the transistor is on, current through R1 and R2 is the same (not sure but I think this is true since the circuit would short circuit).
The Attempt at a Solution
For the first one, I assume that the current through R1 would just be the Voltage/1000 = 8mA.
For the second one, I think the output voltage would just be calculated as Vin*(10^6+10^3)/(10^6) = 5.005 volts. I think that answer would make sense since the transistor is off, so the circuit wouldn't short circuit and we could take R2 into account.