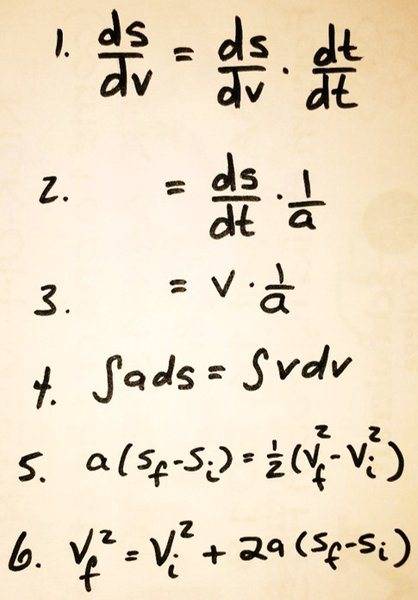SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on the derivation of equations for Uniform Accelerated Motion (UAM), specifically addressing the term ds/dv. The derivation presented is a concise formulation of the acceleration equation: a = dv/dt = (dv/ds)(ds/dt) = v(dv/ds). It clarifies that ds/dv is the reciprocal of dv/ds, although its fundamental significance is minimal. The conversation emphasizes the utility of this derivation in understanding motion dynamics.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Uniform Accelerated Motion (UAM)
- Familiarity with calculus concepts such as derivatives
- Knowledge of kinematic equations
- Basic grasp of physics principles related to motion
NEXT STEPS
- Explore the implications of acceleration in kinematics
- Study the relationship between velocity and distance in motion
- Learn about the graphical representation of UAM
- Investigate advanced topics in calculus related to motion analysis
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, educators teaching kinematics, and anyone interested in the mathematical foundations of motion dynamics will benefit from this discussion.