- #1
tris_d
- 162
- 0
Does inverse square law apply to light in vacuum?
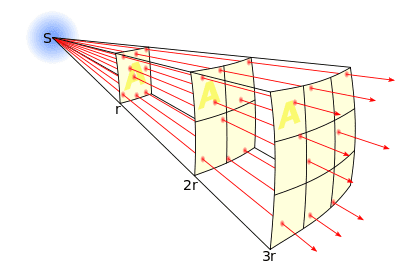
DaleSpam said:Yes.
DaleSpam said:Didn't you get that picture here:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inverse-square_law
It is right in the intro.
tris_d said:Just went there for the picture, and was stupid enough not to read it. Funny!
Light in vacuum refers to the propagation of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum or empty space. In this state, light travels at a constant speed of approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
The inverse square law is a principle in physics that states that the intensity of a physical quantity, such as light, is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source. In other words, as the distance from the source increases, the intensity decreases by a factor of the square of the distance.
Since light travels in a straight line from its source, the intensity of light in a vacuum follows the inverse square law. This means that as the distance from the source increases, the intensity of light decreases according to the square of the distance.
The inverse square law is essential in understanding the behavior of light and its effects on various systems. It is used in fields such as photography, astronomy, and engineering to calculate light intensity, design lighting systems, and determine the distance of objects from a light source.
The inverse square law states that the intensity of light decreases by a factor of the square of the distance from the source. This means that the further away an object is from a light source, the dimmer it will appear. For example, the brightness of a light bulb decreases significantly as you move away from it.