SUMMARY
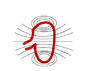
The discussion centers on the magnetic field lines generated by a current-carrying circular loop. Each point on the wire does produce an individual magnetic field, but these fields do not intersect; instead, they add up according to the superposition principle. The Biot-Savart law is referenced to explain how the magnetic field is derived from differential line segments of the current. The representation of magnetic field lines is purely illustrative, serving to visualize the direction and strength of the magnetic field around the conductor.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Biot-Savart law
- Basic knowledge of magnetic fields and their properties
- Familiarity with vector fields and superposition principle
- Concept of magnetic field lines as a representation
NEXT STEPS
- Study the Biot-Savart law in detail to understand its application in calculating magnetic fields
- Explore the concept of magnetic field lines and their representation in diagrams
- Learn about the superposition principle in vector fields
- Investigate the behavior of magnetic fields around different conductor shapes
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electromagnetism, physics educators, and anyone interested in the principles of magnetic fields generated by current-carrying conductors.