SUMMARY
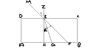
The discussion centers on proving the relationship between the distances d1 and d2 in the context of light refraction, specifically demonstrating that d1/d2 equals the refractive index (μ). Participants reference Snell's Law, stating that sin(i)/sin(r) equals the refractive index, and provide equations involving trigonometric functions to derive this relationship. The user struggles with the mathematical proof despite confirming the relationship experimentally, indicating a need for clearer understanding of trigonometric identities and their application in optics.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Snell's Law in optics
- Familiarity with trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan)
- Basic knowledge of light refraction principles
- Ability to manipulate algebraic equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of Snell's Law using trigonometric identities
- Explore the application of tan() in optics problems
- Investigate the physical implications of changing the refractive index on light behavior
- Practice solving problems involving light refraction in various media
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, optics enthusiasts, and anyone looking to deepen their understanding of light refraction and mathematical proofs in optics.