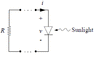pc2-brazil
- 198
- 3
Homework Statement
The current-voltage characteristic of a photovoltaic energy converter (solar cell) shown in the attached figure can be approximated by:
i = I_1(e^{v/V_{TH}} - 1) - I_2
where the first term characterizes the diode in the dark and I2 is a term that depends on light intensity.
Assume I_1 = 10^{-9} and assume light exposure such that I_2 = 10^{-3}\ A.
If it is desired to maximize the power that the solar cell can deliver to a resistive load, determine the optimum value of the resistor. How much power can this cell deliver?
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
This question doesn't provide any value for VTH, but the book mentions that diodes tipically have VTH = 0.025 V, so I assume it is the value to be used here.
Applying KVL to the attached figure:
v+Ri=0
The question asks for the value of R for which P=Ri^2 is a maximum, so I suppose I should differentiate P with respect to R. However, I first need to solve v+Ri=0 and i = I_1(e^{v/V_{TH}} - 1) - I_2 simultaneously in order to find i in terms of R, and it doesn't appear to be possible analytically.
Any hint on how to continue?
Thank you in advance.