- #1
Amaelle
- 310
- 54
Good day , i have an issue with the derivation of the mutual inductance of coil inside solenoid formula
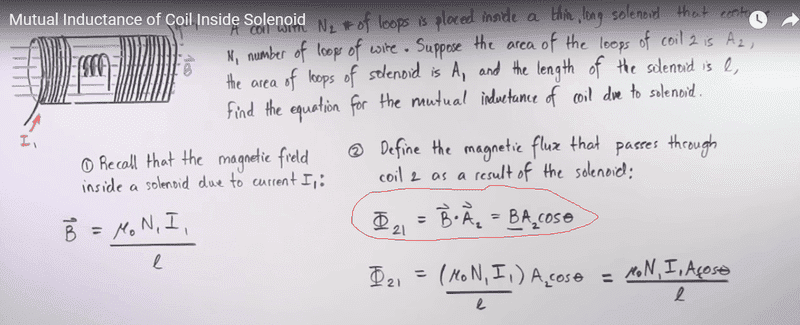
I1 is an alternating current which means that B is varying, and we know that the Flux 21 is equal to the integral of the dot product of B and A2 but as B is varying we CAN NOT take it out of the integral and use the form used in the pic (the formula encercled in red).
Maybe there is something missing in my logic and any help would be highly appreciated, thanks!
I1 is an alternating current which means that B is varying, and we know that the Flux 21 is equal to the integral of the dot product of B and A2 but as B is varying we CAN NOT take it out of the integral and use the form used in the pic (the formula encercled in red).
Maybe there is something missing in my logic and any help would be highly appreciated, thanks!