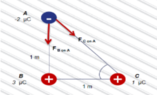
Net Force of A: Diagram Analysis
Click For Summary
Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around determining the net force acting on point A as depicted in a diagram. The subject area pertains to forces and vector analysis in physics.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Problem interpretation
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are attempting to clarify the specific requirements for finding the net force on A, with some asking for further details about the original poster's needs for explanation. There is mention of relevant equations for calculating forces and their components.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants providing guidance on the approach to take, such as identifying vector forces and summing them. There is an invitation for the original poster to share their work for further assistance.
Contextual Notes
There is a reference to a diagram that is essential for understanding the problem, but it is not provided in the thread. The original poster has reiterated the problem statement multiple times, indicating a focus on the net force calculation.
Similar threads
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 12 ·
- · Replies 24 ·
- · Replies 6 ·