theanswerai
- 4
- 1
- Homework Statement
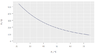
- The attached graph_1 represents the resistance R of a specific NTC thermistor as a function of its temperature ϑ. In the attached graph_2, the heat dissapation P of the thermistor at room temperature of 22 ˚C is displayed as a function of temperature of the thermistor.
Determine the maximum voltage that may be applied to the thermistor to prevent it from heating up above 65 ˚C!
Assume that the thermistor is initially at room temperature.
- Relevant Equations
- heat dissapation
I couldn't solve this problem. Any tips or help would be appreciated. If I am violating against any rules please comment, as this is my second post :-).