Discussion Overview
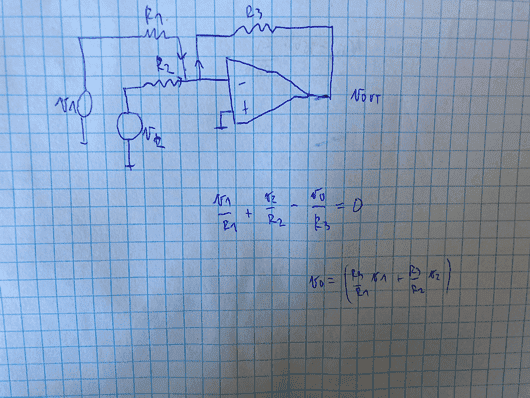
The discussion revolves around the analysis of an operational amplifier (op-amp) adder circuit, specifically focusing on the origin of the negative sign in the output voltage equation. Participants explore the application of Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) in this context, addressing current flow and polarity at a node in the circuit.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- Some participants express confusion about the negative sign in the output voltage equation, questioning its origin and the direction of current flow from the resistor R3.
- One participant suggests that when the input voltage increases, the output of the op-amp must decrease to maintain the virtual ground at the negative input.
- Another participant emphasizes the importance of consistent polarity when applying KCL, noting that all currents flowing into a node should sum to zero.
- There is a discussion about whether the sum of currents flowing into the node equals the sum of currents flowing out, with some participants asserting that the currents should flow to R3.
- One participant clarifies that if currents are defined as flowing into the node, any current flowing out must be assigned a negative sign in the KCL equation.
- Several participants agree on the utility of consistently writing KCL equations with all current arrows pointing into the node to avoid sign errors.
- Concerns are raised about the complexity of defining all currents in more complicated networks, with a note on the potential for errors in both KCL and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) applications.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the need for consistent polarity in KCL equations, but there remains some disagreement about the interpretation of current flow and the implications of the negative sign in the output equation.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight the importance of carefully accounting for current polarities and the potential for errors in circuit analysis, particularly in more complex networks.