Parallel plates - direction of electric field
- Thread starter michaelw
- Start date
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
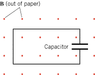
The direction of the electric field between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor is determined by the induced current resulting from a decreasing magnetic field, as explained by Lenz's Law. When the magnetic field decreases, it induces a counteracting current that flows counterclockwise (CCW), leading to a positive charge accumulation on the lower plate and a negative charge on the upper plate. Consequently, the electric field (E field) points upward, from the bottom plate to the top plate. The strength of the E field can be analyzed using Gauss's Law with the formula σ/(2ε₀).
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of Lenz's Law and its application in electromagnetic induction
- Familiarity with the concept of electric fields in capacitors
- Knowledge of Gauss's Law for calculating electric fields
- Basic principles of magnetic fields and their changes over time
- Study Lenz's Law in detail to understand induced currents
- Learn how to apply Gauss's Law for different charge distributions
- Explore the relationship between electric fields and magnetic fields in electromagnetic theory
- Investigate the behavior of capacitors in varying magnetic environments
Physics students, electrical engineers, and anyone interested in understanding electromagnetic induction and capacitor behavior in changing magnetic fields.