SUMMARY
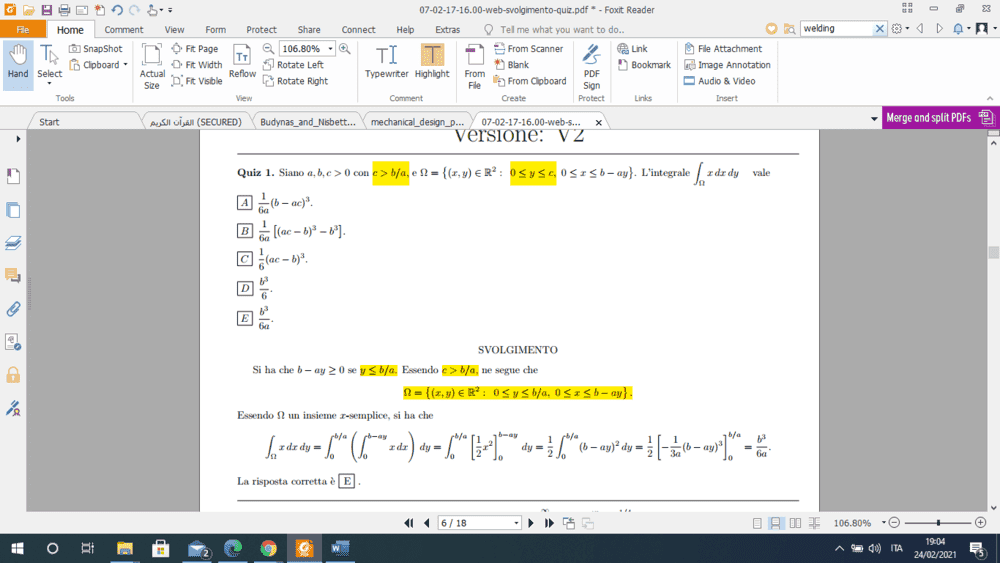
The discussion focuses on the proper setting of integration limits for a triangular area defined by the vertices (0,0), (0, b/a), and (b,0). Participants clarify that the upper limit of the outer integral can be set to b/a instead of c, as c is greater than b/a and does not affect the integral's calculation. The confusion arises from the inclusion of c in the problem statement, which is deemed unnecessary. This highlights the importance of understanding the geometric interpretation of integration limits.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of double integrals in calculus
- Familiarity with geometric interpretations of integration limits
- Knowledge of triangular regions in the Cartesian plane
- Basic proficiency in mathematical notation and symbols
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of double integrals in calculus
- Learn about geometric interpretations of integration limits
- Explore examples of integrating over triangular regions
- Review common pitfalls in setting integration boundaries
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in mathematics, particularly those studying calculus and integration techniques, as well as anyone involved in solving complex integrals involving geometric regions.