- #1
AxisCat
- 40
- 4
Hi All,
This is a project I started a couple of years ago then got stuck or bored and stopped working on it. I am thinking about picking back up where I left off. I am using a AMS AS7262 color sensor with the following overlapping channels: 450, 500, 550, 570, 600 and 650 nm, each with 40nm FWHM.
I used a Digikröm CM110 Monochromator and stepped through the spectrum in 1nm increments saving the output from the sensor to a file. My light source was a standard 100 watt halogen household bulb. This is what I measured:
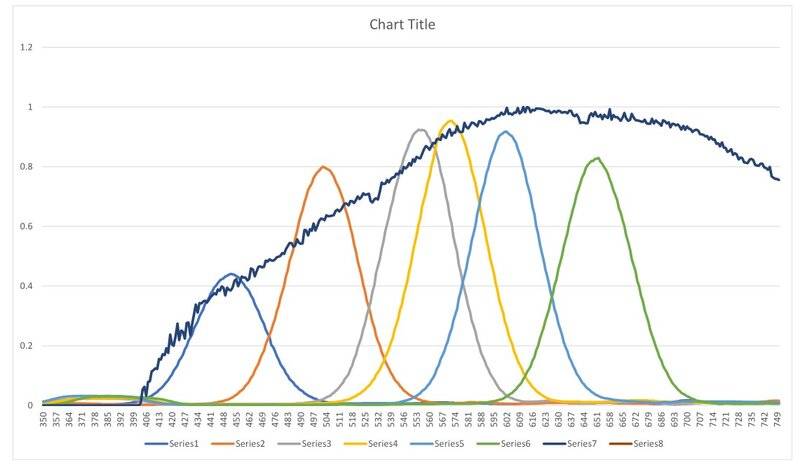
The continuous dark blue curve is from a photodiode I am trying to use as a reference. I understand this is really hard stuff to do with the limited equipment I have available. Is it even possible to recreate a fairly accurate spectral response using just these 6 discrete channels? The manufacturer provides some information that eludes to it being possible.
Anyone have any thoughts?
Thanks,
Axis
This is a project I started a couple of years ago then got stuck or bored and stopped working on it. I am thinking about picking back up where I left off. I am using a AMS AS7262 color sensor with the following overlapping channels: 450, 500, 550, 570, 600 and 650 nm, each with 40nm FWHM.
I used a Digikröm CM110 Monochromator and stepped through the spectrum in 1nm increments saving the output from the sensor to a file. My light source was a standard 100 watt halogen household bulb. This is what I measured:
The continuous dark blue curve is from a photodiode I am trying to use as a reference. I understand this is really hard stuff to do with the limited equipment I have available. Is it even possible to recreate a fairly accurate spectral response using just these 6 discrete channels? The manufacturer provides some information that eludes to it being possible.
Anyone have any thoughts?
Thanks,
Axis