Noone1982
- 82
- 0
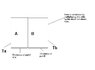
This is not homework, so I think this is the right forum. I am trying to write a program that simulates the heat transfer between, say two cubes of different volumes, heat capacities and thermal resistances.
I know Newton's law of cooling just works dandy for say an object cooling in a fixed enviroment. My questions include: how does this extend to two bodies exchanging heat between boundaries of different thermal resistances?
I know Newton's law of cooling just works dandy for say an object cooling in a fixed enviroment. My questions include: how does this extend to two bodies exchanging heat between boundaries of different thermal resistances?