- #1
elektro2021
- 6
- 0
New poster has been reminded to always show their work when starting schoolwork threads
- Homework Statement
- Size and simulate the circuit (IMAGE BELOW) so that it achieves a 100 ps delay (50-50) using 0.25 μm devices, while driving a 100 fF load on both differential outputs. (VDD = 2.5V) Assume A, B and their complements are available as inputs.
- Relevant Equations
- vailable common data for nmos are following Vt=0.43(V),Vdsat=0.63(V),k'=115x10^-6 (A/V^2),lambda=0.06(v^-1)
I need help for following exercise from Rabaey - Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective
Size and simulate the circuit (IMAGE BELOW) so that it achieves a 100 ps delay (50-50) using 0.25 μm devices, while driving a 100 fF load on both differential outputs. (VDD = 2.5V) Assume A, B and their complements are available as inputs.
Available common data for nmos are following Vt=0.43(V),Vdsat=0.63(V),k'=115x10^-6 (A/V^2),lambda=0.06(v^-1)
Please help me.
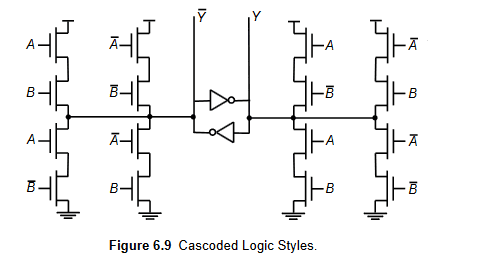
Size and simulate the circuit (IMAGE BELOW) so that it achieves a 100 ps delay (50-50) using 0.25 μm devices, while driving a 100 fF load on both differential outputs. (VDD = 2.5V) Assume A, B and their complements are available as inputs.
Available common data for nmos are following Vt=0.43(V),Vdsat=0.63(V),k'=115x10^-6 (A/V^2),lambda=0.06(v^-1)
Please help me.