lostfan176
- 33
- 0
i really need help with my homework if people can help lead me to the answer it would be really helpful. so far i was only able to do number 1
1) If 2.00 mol of an ideal gas, initially at 1.53 atm and 280 K, is allowed to expand isothermally under
a constant external pressure of 0.920 atm until the final internal pressure is 0.920 atm, what is the
work done?
my answer: -2368 J
2) If the gas involved is ideal and the process is reversible, obtain an expression for w (work), using
our ‘regular’ thermodynamic variables, P, V, n, and T.
3) For which of these systems is the system’s energy conserved in every process: (a) a closed system;
(b) an open system; (c) an isolated system; (d) a system enclosed in adiabatic walls? Please provide
a brief explanation for your answer.
5) We showed ΔH = q for a constant-pressure process. Consider a process in which P is not constant
throughout the entire process, but for which the final and initial pressures are equal. Need ΔH be
equal to q here? (Hint: One way to answer this is to consider a cyclic process)
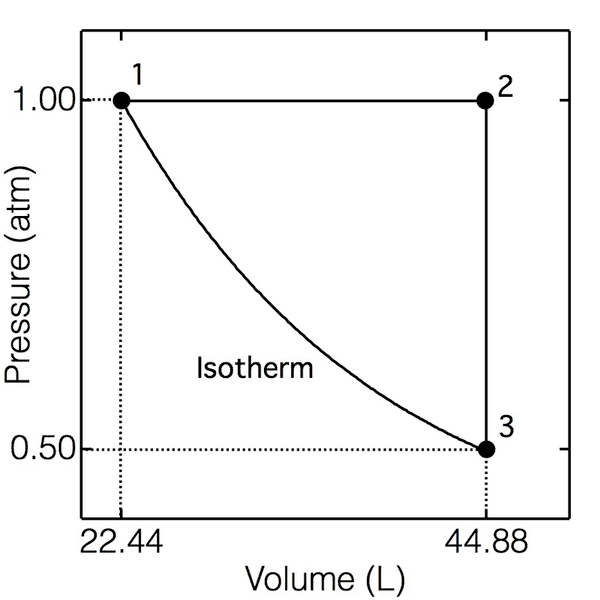
6) A sample consisting of 1.00 mol of a monatomic perfect gas (for which CV,m = 3/2R) is taken
through the cycle shown below. (a) Determine the temperatures at 1, 2, and 3; (b) Calculate q, w,
ΔU, and ΔH for each step and the overall cycle. If a numerical answer cannot be obtained, then
write +, -, or ? as appropriate.
7) 2.50 mol of an ideal gas with CV,m = 12.47 J mol-1 K-1 is expanded adiabatically against a constant
external pressure of 1.00 bar. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas are 325 K and 2.50
bar, respectively. The final pressure is 1.25 bar. Calculate the final temperature, q, w, ΔU, and ΔH.
1) If 2.00 mol of an ideal gas, initially at 1.53 atm and 280 K, is allowed to expand isothermally under
a constant external pressure of 0.920 atm until the final internal pressure is 0.920 atm, what is the
work done?
my answer: -2368 J
2) If the gas involved is ideal and the process is reversible, obtain an expression for w (work), using
our ‘regular’ thermodynamic variables, P, V, n, and T.
3) For which of these systems is the system’s energy conserved in every process: (a) a closed system;
(b) an open system; (c) an isolated system; (d) a system enclosed in adiabatic walls? Please provide
a brief explanation for your answer.
5) We showed ΔH = q for a constant-pressure process. Consider a process in which P is not constant
throughout the entire process, but for which the final and initial pressures are equal. Need ΔH be
equal to q here? (Hint: One way to answer this is to consider a cyclic process)
6) A sample consisting of 1.00 mol of a monatomic perfect gas (for which CV,m = 3/2R) is taken
through the cycle shown below. (a) Determine the temperatures at 1, 2, and 3; (b) Calculate q, w,
ΔU, and ΔH for each step and the overall cycle. If a numerical answer cannot be obtained, then
write +, -, or ? as appropriate.
7) 2.50 mol of an ideal gas with CV,m = 12.47 J mol-1 K-1 is expanded adiabatically against a constant
external pressure of 1.00 bar. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas are 325 K and 2.50
bar, respectively. The final pressure is 1.25 bar. Calculate the final temperature, q, w, ΔU, and ΔH.
Last edited: