SUMMARY
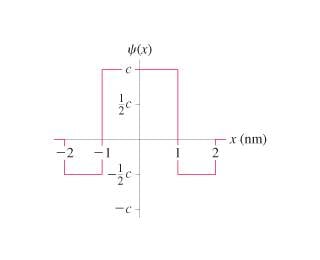
The discussion focuses on determining the normalization constant 'c' for a wavefunction graph, specifically using the integral of the squared wavefunction. The integral from -1 to 1 yields the equation 2/3 = 2c², leading to the conclusion that c = sqrt(1/3) = 0.58 nm-1/2. Participants clarify that the area under the squared wavefunction must be considered to compute probabilities, with the total area equating to 1. The probability of finding the particle between -1 and 1 nm is calculated as the integral of psi squared over that interval.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of wavefunction normalization in quantum mechanics
- Familiarity with integral calculus, particularly definite integrals
- Knowledge of probability density functions in quantum mechanics
- Ability to interpret graphical representations of mathematical functions
NEXT STEPS
- Study the concept of wavefunction normalization in quantum mechanics
- Learn about the properties of integrals, specifically in the context of probability density functions
- Explore piecewise functions and their applications in quantum mechanics
- Investigate the implications of probability calculations in quantum mechanics, including expected values
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in physics, particularly those specializing in quantum mechanics, as well as anyone involved in mathematical modeling of wavefunctions and probability calculations.