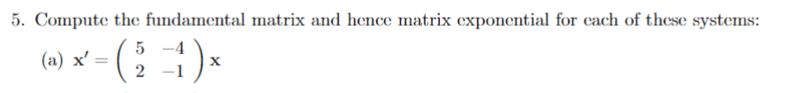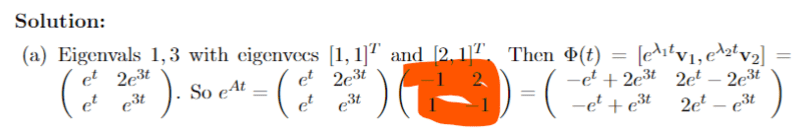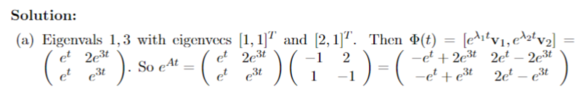Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around solving a system of differential equations using matrix exponentials, specifically focusing on the transformation of the coefficient matrix into its Jordan normal form and the implications of this transformation on the solution process.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants explore the transformation of the original matrix A into its Jordan normal form to facilitate the computation of the matrix exponential. Questions are raised about the origin of the coefficient matrix and the process of finding its inverse, as well as the fundamental matrix's relationship to the solution.
Discussion Status
Several participants are engaging with the concepts of matrix transformations and their applications in solving differential equations. Guidance has been offered regarding the Jordan normal form and the fundamental matrix, but there is no explicit consensus on the specific details of the transformations or their implications.
Contextual Notes
Participants are navigating the complexities of matrix exponentials and transformations, with some expressing confusion about the relationship between the original system and the transformed matrices. There is an emphasis on understanding the definitions and roles of various matrices involved in the solution process.