carnot cycle
- 23
- 0
Homework Statement
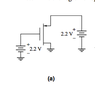
The threshold voltage (Vtp) of this p-channel transistor is -0.4V. Determine the region of operation of this transistor.
Homework Equations
Vsg + Vtp = Vsd(sat)
The Attempt at a Solution
Since the gate-source voltage is 0V, and the threshold voltage is -0.4V, the saturation voltage should be -0.4V. The source is at 2.2V, and the drain terminal is connected to ground potential. Because this Vsd is greater than the saturation voltage that I found using the above equation, I thought this transistor was in saturation mode. However, the book's answer says that the transistor is in cutoff because the gate-source voltage is zero.
I thought that if the gate-source voltage (0V) is greater than the threshold voltage (-0.4V), the transistor could not be in cutoff.
Any help would be greatly appreciated. This seems like a very easy problem, but I have just started studying transistors so I am still trying to conceptually grasp them.