Eucliwood
- 17
- 0
Mentor Note -- Thread moved from the technical forums, so no Homework Template is shown.
So, we've conducted an experiment on resistors in a circuit. The theoretical calculation was based of on E-24 series color band table and the measured resistance of the resistor was measured by a meter. We've identified each percent error, and I happen to noticed that as the theoretical resistance value increases so does the percent error. Why is that? Along with the theoretical vs measured in series the percent error is higher than of the parallel. I was just trying to get a hint so that I can relate other laws regarding it and make my interpretation on the observation. Thank you in advance! I only have three here, i have 3 other with my friend and i also did my own experimentation.
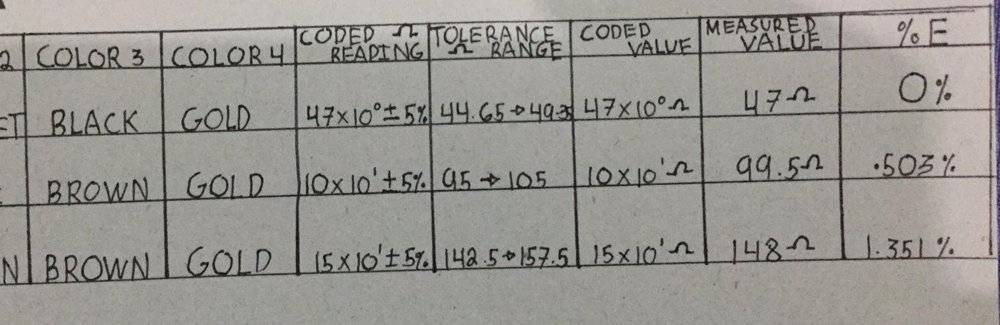
So, we've conducted an experiment on resistors in a circuit. The theoretical calculation was based of on E-24 series color band table and the measured resistance of the resistor was measured by a meter. We've identified each percent error, and I happen to noticed that as the theoretical resistance value increases so does the percent error. Why is that? Along with the theoretical vs measured in series the percent error is higher than of the parallel. I was just trying to get a hint so that I can relate other laws regarding it and make my interpretation on the observation. Thank you in advance! I only have three here, i have 3 other with my friend and i also did my own experimentation.
Last edited by a moderator: