Maybe_Memorie
- 346
- 0
Thermodynamics -- PV Diagram of an Ideal Gas
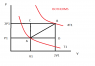
Right, I've got a PV diagram attached to make this easier to explain. The substance is an ideal gas.
I need to calculate the heat absorbed along the different paths ACB, ADB and AB. The first two are easy. The red lines in the diagram are isotherms.
PV = NKT for an ideal gas.
QAB = ΔU + ΔW = ΔU + PΔV, U is internal energy, U = U(T) = CVT
For a monatomic ideal gas, CV = 3/2
The change in internal energy is obviously just 3/2NK(4T1 - T1) = 9/2NKT1
The work done is P1(2V1 - V1) = NKT1
Thus the heat absorbed on the path AB is 11/2NKT1. My problem is the solution manual says it's 6NKT1.
It also says that ΔU + ΔW = 3/2(NK)(2T1) + 3/2P1V1 = 6NKT1 which obviously isn't true so I'm questioning it's integrity. It uses the fact that QAB = 6NKT1 in the proceeding problems as well so it's a little confusing.
Thanks for any help.
Homework Statement
Right, I've got a PV diagram attached to make this easier to explain. The substance is an ideal gas.
I need to calculate the heat absorbed along the different paths ACB, ADB and AB. The first two are easy. The red lines in the diagram are isotherms.
Homework Equations
PV = NKT for an ideal gas.
QAB = ΔU + ΔW = ΔU + PΔV, U is internal energy, U = U(T) = CVT
For a monatomic ideal gas, CV = 3/2
The Attempt at a Solution
The change in internal energy is obviously just 3/2NK(4T1 - T1) = 9/2NKT1
The work done is P1(2V1 - V1) = NKT1
Thus the heat absorbed on the path AB is 11/2NKT1. My problem is the solution manual says it's 6NKT1.
It also says that ΔU + ΔW = 3/2(NK)(2T1) + 3/2P1V1 = 6NKT1 which obviously isn't true so I'm questioning it's integrity. It uses the fact that QAB = 6NKT1 in the proceeding problems as well so it's a little confusing.
Thanks for any help.