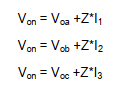Discussion Overview
The discussion focuses on the terminology and notation related to voltage potential, specifically the interpretation of voltage measurements and the application of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL). Participants express confusion over the notation used and the implications of reference points in voltage measurements.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
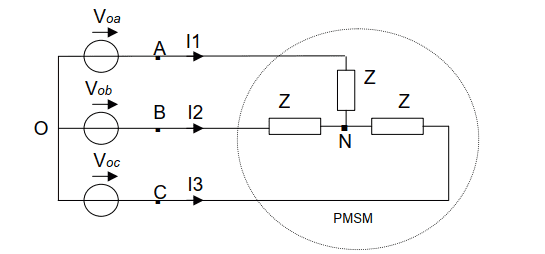
- Some participants seek clarification on whether Voa represents the voltage of point "o" with respect to point "a".
- It is noted that all voltage measurements are relative to a reference node, often referred to as 'Ground', which may not be physically connected to the Earth.
- One participant emphasizes the importance of consistency in sign definitions when applying KVL, suggesting that correct answers depend on this consistency.
- Another participant raises concerns about the notation used in KVL equations, arguing that it may not align with common practices and could lead to errors if sign conventions are not followed.
- There is a mention that definitions of voltage polarities can be arbitrary, but consistency within a single analysis is crucial.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying levels of agreement on the interpretation of voltage potential and the notation used. While some agree on the importance of consistency in analysis, there is no consensus on the definitions and practices surrounding voltage measurements.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight that the definitions of voltage and reference points can vary, and the discussion reflects different interpretations and practices in electrical engineering. There are unresolved questions regarding the notation and its implications for circuit analysis.