SUMMARY
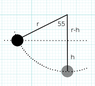
The discussion revolves around calculating the length of a pendulum arm given a bob mass of 2.0 kg, an angle of 55 degrees, and a maximum speed of 3.5 m/s. The kinetic energy (Ek) is calculated as 12.25 J using the formula Ek = 1/2mv^2. The potential energy (Ep) is expressed as Ep = mgh, leading to a height (h) of 0.625 m. To find the length of the pendulum arm, the relationship between the height and the angle is established using trigonometric functions, specifically cosine, to derive the length (r) of the pendulum arm.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of kinetic energy and potential energy equations (Ek = 1/2mv^2, Ep = mgh)
- Basic knowledge of trigonometry, particularly cosine and sine functions
- Ability to solve algebraic equations
- Familiarity with pendulum motion concepts
NEXT STEPS
- Study trigonometric relationships in right triangles, focusing on cosine and sine laws
- Learn how to apply energy conservation principles in pendulum problems
- Practice solving for unknowns in physics equations involving angles and lengths
- Explore pendulum dynamics and the effects of varying angles on motion
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and energy conservation, as well as educators seeking to clarify pendulum motion concepts.