Homework Help Overview
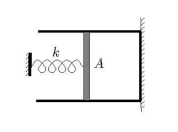
The discussion revolves around the volume-pressure relationship for an expanding ideal gas, particularly in the context of a gas being heated slowly while contained within a system involving a spring and a piston. Participants are exploring the implications of atmospheric pressure on the system and the correct application of relevant equations.
Discussion Character
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are attempting to derive the relationship between pressure and volume using equations related to spring mechanics and the ideal gas law. Questions arise regarding the assumptions made about atmospheric pressure and the initial conditions of the gas, particularly concerning temperature and volume.
Discussion Status
There is an ongoing exploration of the problem with various interpretations being discussed. Some participants have offered insights into the implications of ignoring atmospheric pressure, while others are questioning the validity of the assumptions regarding temperature and the state of the gas. Guidance has been provided regarding the relationship between pressure and volume, but no consensus has been reached.
Contextual Notes
Participants are navigating constraints such as the assumption of zero atmospheric pressure and the implications of this on the behavior of the gas and the spring system. There is also a discussion about the initial conditions of the gas and the geometric considerations of the system.