SUMMARY
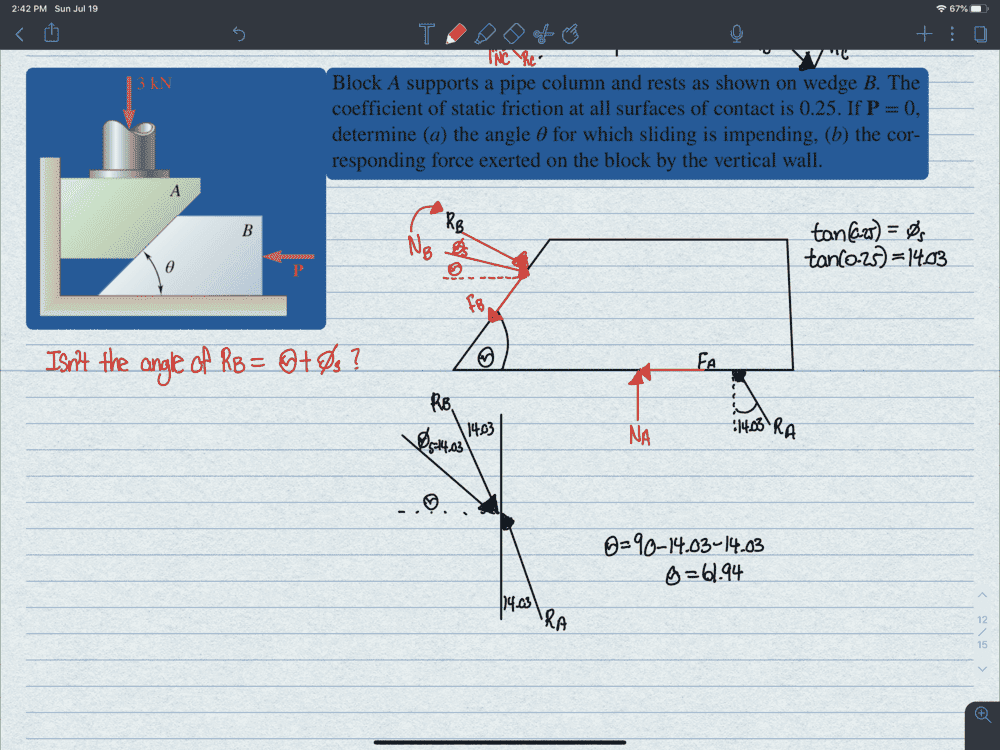
The correct angle for the wedges problem is established at 28.1 degrees. The analysis involves understanding the relationship between the normal force (## F_N ##) acting on wedge B and the frictional forces at play. By considering wedge B as massless, the solution simplifies to the expression ## \tan{\theta}=\sin{\theta}/\cos{\theta} ##. Additionally, excluding gravity and the masses of the wedge and block can clarify the problem, particularly when visualizing the system on a horizontal frictionless table.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent)
- Familiarity with Newton's laws of motion
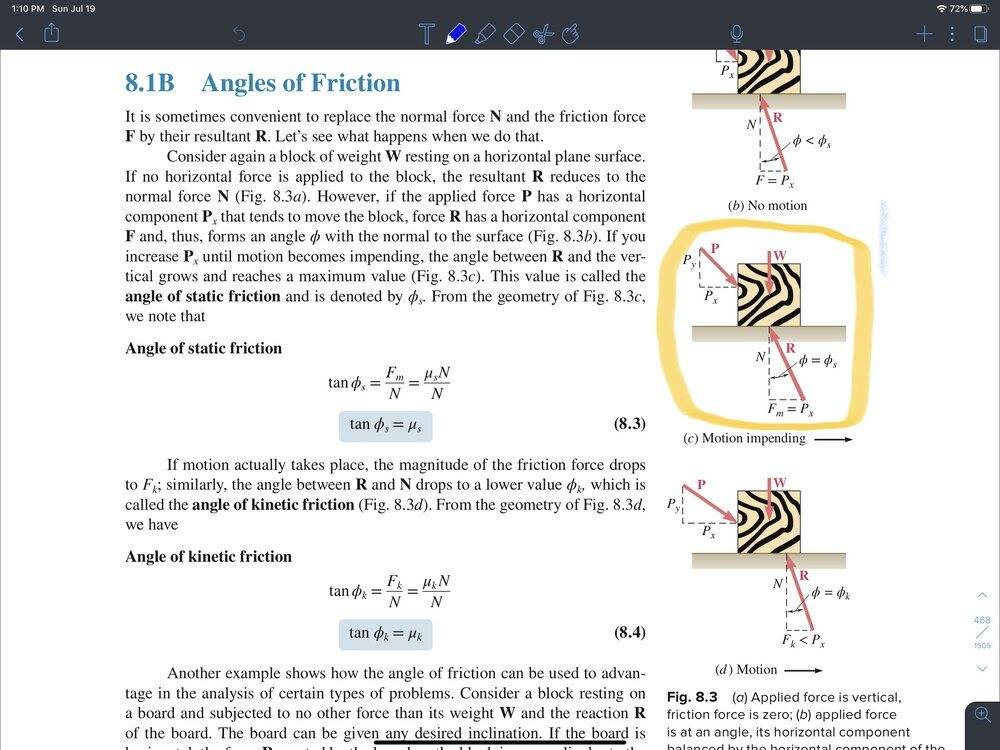
- Knowledge of frictional forces and their maximum values (## F_F = \mu F_N ##)
- Concept of normal force in physics
NEXT STEPS
- Research the implications of massless objects in physics problems
- Study the effects of friction on inclined planes
- Learn about the application of trigonometric identities in physics
- Explore the concept of systems on frictionless surfaces in classical mechanics
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and friction, as well as anyone solving problems related to inclined planes and forces.