Marioweee
- 18
- 5
- Homework Statement
- We have a divergent lens on which a beam of parallel rays strikes from left to right. Part of the light reflects off the first face and the reflected rays converge at the point indicated by the arrow, which is - 25.5 cm from the vertex of the first lens surface. Assuming that the lens is symmetrical, that is, that "R1= -R2 &, which is thin, and whose refractive index is 1.5, state the value of the focal point of the lens with its sign.
- Relevant Equations
- ---
I have recently started with geometric optics and I do not quite understand what this problem asks of me. According to the statement, the focal point of the lens would be -25.5cm, right? That is, it is only a problem of concepts where it is not necessary to take into account the radii of the lenses or the refractive index, right?
Maybe I am very wrong that is why I ask for some help.
This is the picture of the problem that I have done.
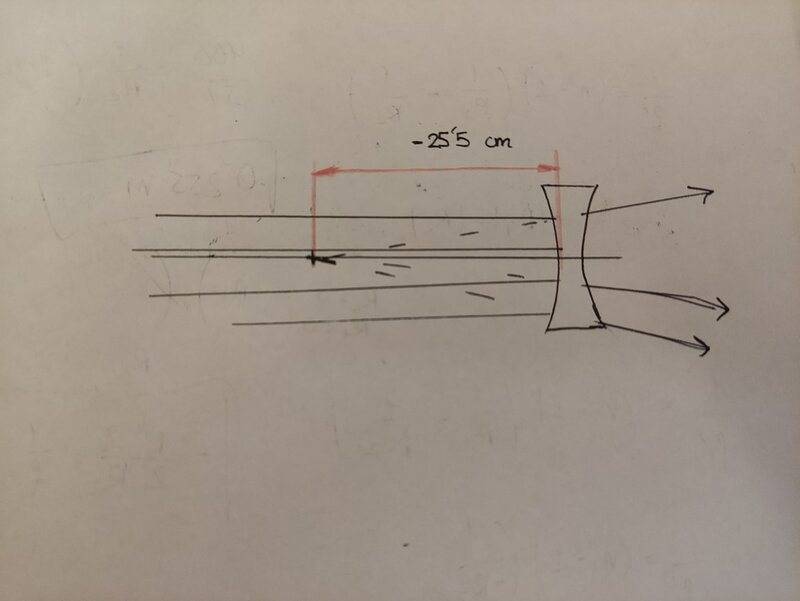
Maybe I am very wrong that is why I ask for some help.
This is the picture of the problem that I have done.