teegribb
- 1
- 0
I am aware of what positive and negative polarities are but what specifically causes the distinction between positive and negative polarity?
The discussion focuses on the distinction between positive and negative polarities, particularly in the context of electric charge on particles such as protons and electrons. It highlights that Benjamin Franklin established the convention of labeling charges as positive and negative, a decision made before the discovery of electrons. The negative charge of electrons is quantified as -1.6021766208(98)×10-19 coulombs, which can confuse learners due to the flow of electricity being attributed to negatively charged electrons moving from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a circuit.
PREREQUISITESThis discussion is beneficial for physics students, educators, electrical engineers, and anyone interested in the foundational concepts of electricity and charge polarity.
Welcome to the PF.teegribb said:I am aware of what positive and negative polarities are but what specifically causes the distinction between positive and negative polarity?
There may be a very simple answer to satisfy you.teegribb said:Charge on particles specifically. For example electrons and protons are negative and positive respectively but these are simply names. What is different about a protons positive charge to an electrons negative charge?
Hey I can't help but rattle your cage on this. I looked and looked but couldn't find any polarized resistors in my collection.berkeman said:Welcome to the PF.
What is the context of your question? Polarity of what? Of a capacitor or a resistor, as in electronics? Or as charge on particles?
 LOL
LOL
LOL. I meant it in the context of the + and - sides of the resistor that has a DC current flowing through it.Averagesupernova said:couldn't find any polarized resistors
The Greek word for amber is electron...sophiecentaur said:The choice of which sign to choose for a charged glass rod or a charged piece of amber or from one particular terminal on an early chemical battery was quite (afaik) arbitrary.
It has too do with current in the circuit the resistor is found in. And the reference point for identifying the polarity is the power source. The end of the resistor that is connected to the negative terminal of the battery is negative when the other end is connected to the positive terminal of the battery.Averagesupernova said:You know I am not above learning something. I thought maybe there was something about resistors that I did not know yet.
The choice of the sign was long before the electron was found and named. The name was fitted to the fact, in retrospect.Svein said:The Greek word for amber is electron...
Hang on a bit. They hadn't discovered electrons (and didn't know much at all about Electricity) when the + and - signs were allocated to the batteries that they made. They had no real idea about the Chemistry of how the batteries worked.Jon B said:It seems the source of electrons was determined and labeled Negative and home was labeled positive.
Also, what they saw was referred to "Cathode Rays" and it was not identified as a stream of particles until even later.Jon B said:Connecting a battery negative terminal to the hot plate and positive to the cold plate enhanced the electron flow
sophiecentaur said:Hang on a bit. They hadn't discovered electrons (and didn't know much at all about Electricity) when the + and - signs were allocated to the batteries that they made. They had no real idea about the Chemistry of how the batteries worked.
Your are post hoc rationalising the situation. If 'they' had decided to call the metal electrode of a Leclanche cell "positive" then it would have turned out that the electron was a positive particle- once it had been found.
Yes, on the face of it but having electrons with a negative charge does make people stop and think and it must help to discourage the very Mechanical picture that people risk getting in their heads about Electricity.anorlunda said:Franklin's choice of which pole was negative would be one thing I would love to change.
And where would the early workers have got hold of a controllable "powerful electron spark" if they didn't know about electrons? You can't use modern arguments if you want to put yourself in the shoes of ancient Scientists.Jon B said:It seems like arbitrary labeling is based on the triboelectric charge and its behavior relative to objects around it. Imagine working with lightning instead of Amber. A powerful electron spark will leave a small pit on polished graphite if the graphite is positively charged with respect to the source of the spark.
sophiecentaur said:And where would the early workers have got hold of a controllable "powerful electron spark" if they didn't know about electrons? You can't use modern arguments if you want to put yourself in the shoes of ancient Scientists.
Wikipedia said:In 1750, he [Franklin] published a proposal for an experiment to prove that lightning is electricity by flying a kite in a storm that appeared capable of becoming a lightning storm.
anorlunda said:I know that each country's education tends to focus on its own national heroes. But can it be that you never heard of Franklin's kite and key, and Leyden jar Sophie?
Lightning was a good source but not controllable so observing electrostatic effects in the dark room or in a nightime lightning strike that "negated" its target must have been fascinating... But what can we tell the op about the difference? The cause of the distinction between them in electricity is a testable fact that allows students and inventors to have standards to work with related to the negatively charged particles that can be easily manipulated to do "work."sophiecentaur said:And where would the early workers have got hold of a controllable "powerful electron spark" if they didn't know about electrons? You can't use modern arguments if you want to put yourself in the shoes of ancient Scientists.
There is that burning question about which direction the electrons jump during a lighning strike.anorlunda said:I know that each country's education tends to focus on its own national heroes. But can it be that you never heard of Franklin's kite and key, and Leyden jar Sophie?

The lightning thing was a reponse to your question, where did they get a powerful spark?sophiecentaur said:You are missing my point entirely. Franklin did not know about electrons so how could he have come to any conclusion, based on electrons? He knew nothing of the mechanism of the conduction of electricity by electrons. His lightning source was just a 'black box' for him.
Wikipedia said:Franklin's discoveries resulted from his investigations of electricity. Franklin proposed that "vitreous" and "resinous" electricity were not different types of "electrical fluid" (as electricity was called then), but the same electrical fluid under different pressures. He was the first to label them as positive and negative respectively, and he was the first to discover the principle of conservation of charge.
sophiecentaur said:I wonder whether any well informed PF Chemists could suggest a better than arbitrary reason for the signs. Could it be anything to do with Adding or Subtracting some element in an electrolytic cell - like you get Hydrogen 'taken out of' water at the (-) Cathode?
Fluid Theories
The information presented below is drawn from R.A.R. Tricker's book "Early Electrodynamics: The First Law of Circulation" and "A History of the Theories of Aether and Electricity," by E.T. Whittaker.
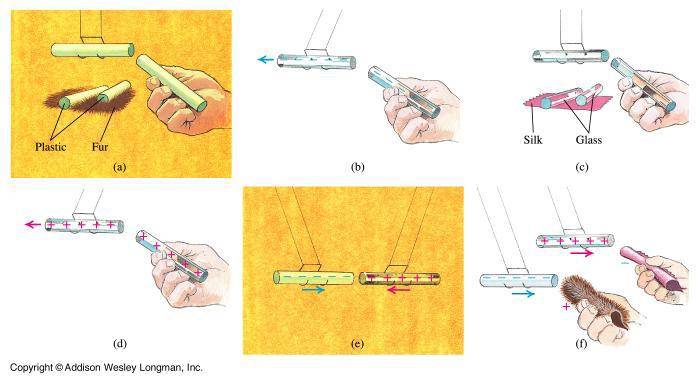
Du Fay observed that bodies could be electrified in two different ways, depending on the materials used. He classified materials into two groups- "vitreous" and "resinous." Vitreous materials included glass, crystal, gems, hair, and wool, whereas resinous materials included amber, copal (a resin less aged than amber), silk, thread, and paper. The first class when electrified by rubbing was said to have vitreous electricity, whereas objects of the second class would have resinous electricity. Objects that with vitreous electricity repelled each other, but attracted those with resinous electricity. Thus was formed the two-fluid theory of electricity, which stated that electricity was essentially vitreous and resinous fluid which possessed powers of attraction and repulsion.
You have missed out the operative word "electron" that was in my question. If they didn't know about electrons then they couldn't have knows what they were getting in their lightning strike. (The "two fluid' theory seems to have been in operation at the time). And that is the point I have made several times. Nothing in the history of science could involve the electron until it had been discovered.anorlunda said:The lightning thing was a reponse to your question, where did they get a powerful spark?
sophiecentaur said:I can't see, in your attachment, anything to suggest that the choice of sign was anything other than arbitrary.
That's true but why did electrons creep into the following description of what he was (or thought he was ) doing?anorlunda said:I'm sorry Sophie. I thought it was implicit that Franklin's choice of polarity was arbitrary. That's why I joked that I would like to have changed that choice if I had a time machine.
YesJon B said:Is negative an abundance of electrons and positive a depletion?
We don't "know" we 'agree'.Jon B said:So how do we know today what is negative and positive.
teegribb said:I am aware of what positive and negative polarities are but what specifically causes the distinction between positive and negative polarity?